|
Child level |
|
|
|
Same level |
|
|
|
Genera |
|
|
|
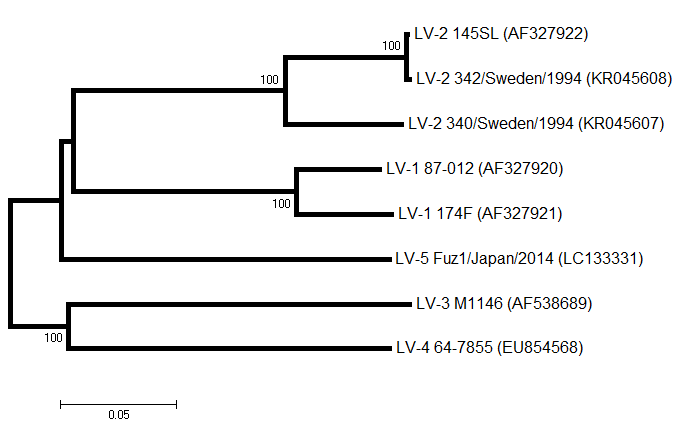
Ljungan virus types 1 to 6 belong to the species Parechovirus B, genus Parechovirus. The partial genome sequence of a virus isolated from bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus) was originally determined by Niklasson et al. (1998) (accession no. AF020541). 597 nt of the 5' untranslated region plus 1521 nt of the capsid-coding region (VP0 and VP3) were determined for the new agent called Ljungan virus (LV; isolate 145SL). More recently the complete genome sequences of four Ljungan virus isolates have been determined (Johansson et al., 2002; 2003). Comparisons with other picornaviruses indicate that the capsid-coding genes of LV are most closely related to human parechovirus types 1 and 2 (formerly echovirus types 22 and 23), members of the newly created picornavirus genus, Parechovirus. In April 2003, the (nearly) complete genome sequence of an American Ljungan virus was reported (Johansson et al., 2003; AF538689). In 2016 a fifth type of Ljungan virus was found in gulls (Larus sp.) in Japan (Mitake et al., 2016). Search for Ljungan virus sequences on GenBank Genome organisation
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic tree (Neighbor-joining) showing the relationships between the parechoviruses (VP1 nucleotide p-dist) (N.J. Knowles, unpublished).
ReferencesJohansson, S., Niklasson, B., Maizel, J. Gorbalenya, A.E. and Lindberg, A.M. (2002). Molecular analysis of three Ljungan virus isolates reveals a new, close-to-root lineage of the Picornaviridae with a cluster of two unrelated 2A proteins.J. Virol. 76: 8920-8930. Niklasson, B., Kinnunen, L., Hornfeldt, B., Horling, J., Benemar, C., Hedlund, K.O., Matskova, L., Hyypiä, T. and Winberg, G. (1999). A new picornavirus isolated from bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus). Virology 255: 86-93. Lindberg, A.M. and Johansson, S. (2002). Phylogenetic analysis of Ljungan virus and A-2 plaque virus, new members of the Picornaviridae. Virus Res. 85: 61-70. Mitake, H., Fujii, Y., Nagai, M., Ito, N., Okadera, K., Okada, K., Nakagawa, K., Kishimoto, M., Mizutani, T., Okazaki, K., Sakoda, Y., Takada, A. and Sugiyama, M. (2016). Isolation of a novel Ljungan virus from wild birds in Japan. J. Gen. Virol. 2016 May 20. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000508. [Epub ahead of print] Wu Z, Lu L, Du J, Yang L, Ren X, Liu B, Jiang J, Yang J, Dong J, Sun L, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zheng D, Zhang C, Su H, Zheng Y, Zhou H, Zhu G, Li H, Chmura A, Yang F, Daszak P, Wang J, Liu Q, Jin Q. Comparative analysis of rodent and small mammal viromes to better understand the wildlife origin of emerging infectious diseases. Microbiome. 2018 Oct 3;6(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0554-9. PubMed PMID: 30285857; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6171170.
|